1).although this interaction is a relative newcomer to the supramolecular chemistry arena, it has a long history. Organic halogen compounds are organic compounds that contain a single or more atom of hydrogen altered by an equivalent number of halogen atoms (f, cl, br, or i).
What Is Halogen In Chemistry, Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine (i), and astatine. The halogens are the elements in group 17 of the periodic table.

Halogens the halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table. Fluorine (f), chlorine (cl), bromine (br), iodine (i), and astatine (at). A halogen is any element on the periodic table of elements that falls into group (or family) 17. The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements.
Fluorine (f), chlorine (cl), bromine (br), iodine (i), and astatine (at).
The halogens are a family of chemical elements that comprise an entire column of the periodic table. These elements are called the halogens (from the greek hals, salt, and gennan, to form or generate) because they are literally the salt formers. The artificially created element 117, tennessine (ts), may also be a halogen. Halogen, any of the six nonmetallic elements that constitute group 17 (group viia) of the periodic table. Halogen atoms can be found in almost any type of organic substance (e.g., alcohols, ketones, and carboxylic acids). (entry 1 of 2) :
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Halogen chemistry, volume 3 focuses on advancement in the study of halogens. Halogen bulbs contain a small amount of halogen gas. The halogen elements are fluorine (f), chlorine (cl), bromine (br), iodine (i), astatine (at), and tennessine (ts). The most commonly found halogens in organic compounds are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. Elements in the halogen group have seven electrons.
 Source: sciencenotes.org
Source: sciencenotes.org
(left to right) chlorine is a gas, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid. What is halo in chemistry? They are located to the right of the other nonmetals and to the left of the noble gases. Definition of ~ s 1) group viia elements: In the modern iupac nomenclature, this group is known as group 17.

For more information, see the related links, below. Group 7 elements form salts when they react with metals. The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table. The halogens, aka halogen family, are a group of reactive elements in group 17 of the periodic table, to the right of the chalcogens, and to the.
 Source: mrseldred.weebly.com
Source: mrseldred.weebly.com
The halogens are the only periodic table group containing elements in all three familiar states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) at standard temperature and pressure. (left to right) chlorine is a gas, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid. Organic halogen compounds are organic compounds that contain a single or more atom of hydrogen altered by an.
 Source: chemizi.blogspot.com
Source: chemizi.blogspot.com
The most commonly found halogens in organic compounds are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. How do you name halo alkanes? What are halogens in chemistry? A halogen is a gas, such as iodine or bromine. Halogens the halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table.
 Source: mydigitalkemistry.com
Source: mydigitalkemistry.com
The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements. The halogens are the elements in group 17 of the periodic table. Many, however, are common in combination with other elements here is a look at the identity of these elements, their location on the periodic table, and their common. What is the halogen group? Group 7 elements form salts when they react.
 Source: alamy.com
Source: alamy.com
Halogen, any of the six nonmetallic elements that constitute group 17 (group viia) of the periodic table. These elements appear in the column just to the left of the noble gases mentioned earlier. The halogens are a family of chemical elements that comprise an entire column of the periodic table. They are reactive nonmetallic elements that form strongly acidic compounds.

What is halo in chemistry? In particular, studies of the interactions of molecular. Many, however, are common in combination with other elements here is a look at the identity of these elements, their location on the periodic table, and their common. The most commonly found halogens in organic compounds are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. Halogens the halogens are a.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Elements in the halogen group have seven electrons in their outer shells giving them many unique properties. The artificially created element 117, tennessine (ts), may also be a halogen. (entry 1 of 2) : They are located to the right of the other nonmetals and to the left of the noble gases. Definition of ~ s 1) group viia elements:
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
The halogens are the only periodic table group containing elements in all three familiar states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) at standard temperature and pressure. They are reactive nonmetallic elements that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen, from which simple salts can be made. None of the halogens can be found in nature in their elemental form. The term.
 Source: physciq.blogspot.com
Source: physciq.blogspot.com
(left to right) chlorine is a gas, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid. The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table. The halogens, aka halogen family, are a group of reactive elements in group 17 of the periodic table, to the right of the chalcogens, and to the left of.
![Chemistry Halogen [PPTX Powerpoint] Chemistry Halogen [PPTX Powerpoint]](https://i2.wp.com/static.fdocuments.in/img/1200x630/reader020/image/20191006/546da58ab4af9fe51b8b4f2e.png?t=1601758656) Source: fdocuments.in
Source: fdocuments.in
These elements appear in the column just to the left of the noble gases mentioned earlier. 1).although this interaction is a relative newcomer to the supramolecular chemistry arena, it has a long history. A halogen has 7 valence electrons. They are located to the right of the other nonmetals and to the left of the noble gases. A halogen is.
 Source: chem.ucla.edu
Source: chem.ucla.edu
Fluorine (f), chlorine (cl), bromine (br), iodine (i), and astatine (at). In fact, halogens are so reactive that they do not occur as free elements in nature. What is the halogen group? The halogens are a family of chemical elements that comprise an entire column of the periodic table. The most commonly found halogens in organic compounds are fluorine, chlorine,.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The halogen elements are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and possibly tennessine. Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine (i), and astatine. They are reactive nonmetallic elements that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen, from which simple salts can be made. Halogen definition, any of the electronegative elements, fluorine, chlorine, iodine, bromine, and astatine, that form binary salts by direct union with metals..
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements. What are halogens in chemistry? 1).although this interaction is a relative newcomer to the supramolecular chemistry arena, it has a long history. Group 7 elements form salts when they react with metals. Halogens the halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The halogens are a family of chemical elements that comprise an entire column of the periodic table. Fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine (i), and astatine. The halogen elements are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine, and possibly tennessine. These elements are called the halogens (from the greek hals, salt, and gennan, to form or generate) because they are literally the salt formers..
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
None of the halogens can be found in nature in their elemental form. Physical states of halogens halogens represents all of the three familiar states of matter: These elements are called the halogens (from the greek hals, salt, and gennan, to form or generate) because they are literally the salt formers. They are located to the right of the other.
 Source: spmchemistry.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
Source: spmchemistry.blog.onlinetuition.com.my
Any of the five elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine that form part of group viia of the periodic table and exist in the free state normally as diatomic molecules. A halogen is a gas, such as iodine or bromine. The halogens are the only periodic table group containing elements in all three familiar states of matter (solid, liquid,.

What are halogens in chemistry? A halogen has 7 valence electrons. They are located to the right of the other nonmetals and to the left of the noble gases. The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements. None of the halogens can be found in nature in their elemental form.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Halogen, any of the six nonmetallic elements that constitute group 17 (group viia) of the periodic table. What is halo in chemistry? The halogens are a family of chemical elements that comprise an entire column of the periodic table. The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements. The artificially created element 117, tennessine (ts), may also be a halogen.
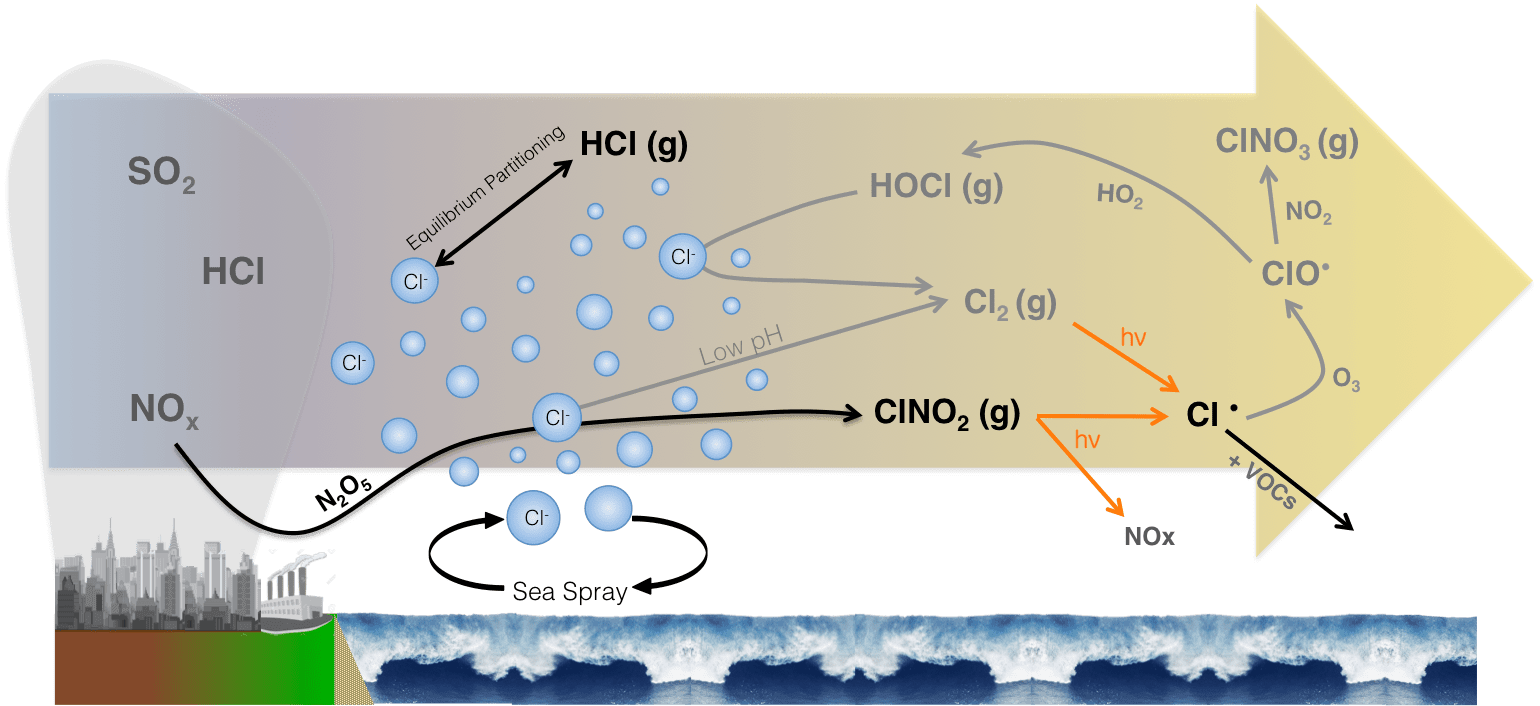 Source: atmos.washington.edu
Source: atmos.washington.edu
(chemistry) forming names of chemical compounds which contain one or more halogen atoms. The halogens are located on the left of the noble gases on the periodic table. The halogens are the only periodic table group containing elements in all three familiar states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) at standard temperature and pressure. 1).although this interaction is a relative.
 Source: aim2destiny.blogspot.com
Source: aim2destiny.blogspot.com
The halogens are highly reactive nonmetallic elements. The most commonly found halogens in organic compounds are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. The halogens are a group of elements in the periodic table. The most commonly found halogens in organic compounds are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. In this regard, what is a halogen in chemistry?
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
A halogen is a gas, such as iodine or bromine. What is halo in chemistry? They are located to the right of the other nonmetals and to the left of the noble gases. (chemistry) forming names of chemical compounds which contain one or more halogen atoms. The halogens are the only periodic table group containing elements in all three familiar.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
The halogens are a family of chemical elements that comprise an entire column of the periodic table. Halogen, any of the six nonmetallic elements that constitute group 17 (group viia) of the periodic table. Physical states of halogens halogens represents all of the three familiar states of matter: The term ‘halogen’ means �salt former�. In the modern iupac nomenclature, this.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Halogen bulbs contain a small amount of halogen gas. They are reactive nonmetallic elements that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen, from which simple salts can be made. These elements appear in the column just to the left of the noble gases mentioned earlier. In the modern iupac nomenclature, this group is known as group 17. These elements are called.








